The AIRR-C Germline Database Working Group (GLDB-WG) was formed in 2016, with an overall mission of promoting the comprehensive and accurate identification, description, classification, annotation, curation, and consistent use of germline IG and TR genes/alleles across species, strains, and populations.
Open-Access Germline Sets
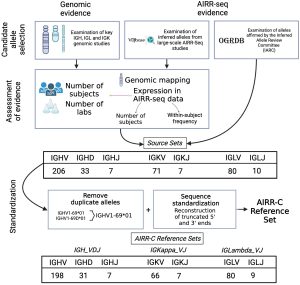
The GLDB-WG has recently released the first human germline sets endorsed and published by the AIRR-C. These germline sets draw on years of policy development, and implement a set of transparent criteria to ensure the inclusion of the most supported alleles, arriving at high quality sets of IG alleles that can be used for accurate AIRR-seq analysis. They are available, free of charge, for unrestricted use in academia and industry. Work is under way to extend the sets to TR loci.
The WG will continue to expand these sets over time as additional alleles are identified by the community.
For more information on these germline sets, please refer to our publication:
In addition to human germline sets, additional sets for mouse are currently also available, and sets for several additional animal model species are also forthcoming.
Policy and Analysis Recommendations
Through the formation of critical partnerships with other AIRR-C working groups/subcommittees and external groups across the immunogenetics field at large, GLDB-WG has made tangible achievements that include policy and analysis recommendations on germline gene/allele curation, naming and standardization. See:
Open-Access Databases
The WG has collaborated on the development of two new open access databases focused on curating and cataloging IG and TR germline variation from various data sources including both AIRR-seq and genomic sequencing.
OGRDB: https://ogrdb.airr-community.org/ (Lees et al. 2020)
VDJbase: https://vdjbase.org/ (Omer et al. 2020)
OGRDB is primarily a platform for the publication of open-access germline sets: both those endorsed by the AIRR-C as supported sets, and others, which are considered to represent best practice for their respective species, while not necessarily meeting the criteria or support levels of the AIRR-C sets. Currently published sets cover frequently-used laboratory strains of the mouse. Work is actively under way to provide sets for other species.
VDJbase is a population-level database of germline sequences, drawn from analysis of over 1600 human repertoires, and 150 annotated assemblies of human genomic loci, with hundreds more to be included by the end of 2024. Analyses can be run interactively on selected samples, and the data is available for download.
Since their inception, OGRDB and VDJbase have been used successfully as a combined discovery platform for identifying new human alleles. And they have more recently expanded support for non-human model organisms as well. Together, these databases allow users to access known IG and TR alleles alongside supporting AIRR-seq and genomic data, facilitating exploration of genetic variation in IG/TR genes and adjacent non-coding regions, and allele frequency data at the population level. Interactive tables and analysis features allow users to generate summary reports for various IG/TR genetic data features, and via OGRDB, users can access expert-curated IG/TR germline datasets in multiple formats for integration into multiple AIRR-seq pipelines.